The safety shoes are designed to ensure personal and workplace safety. As a unique feature, these shoes can prevent cuts, bruises, and abrasions that may occur in the workplace. The CE EN ISO 20345: Safety Shoes Stanard is an extra protective shoe suitable for work requiring high levels of protection.
In this article, we talk about the following; What is CE EN ISO 20345, How to select safety boots standard, and the details of each safety shoe class.
What does EN ISO 20345 mean?
EN ISO 20345:2011 is a European standard for personal protective equipment. This standard specifies the requirements for safety footwear. It applies to all safety footwear types, including steel toecaps, composite toes, and ankle protectors.
EN ISO 20345:2011 was the old revision, followed by PPE Regulation EU 2016/425, the latest version of this standard.
What does PPE EU 2016/425 mean?

PPE regulation EU 2016/425 is the latest version of the safety shoe standard. It was released on December 31, 2016. The previous version of this standard was EN 20345:2011. This standard applies to safety shoes with a steel toe cap and applies to both men’s and women’s shoes.
The fundamental changes in this version are:
- The term “safety footwear” has been replaced with “safety footwear with a steel toe cap” throughout the standard;
- The EN ISO 20345:2011 test method for measuring friction has been replaced by a new test method that uses a pendulum tester to measure friction;
- A new test method for measuring the energy absorption capacity of safety footwear has been added;
- New requirements for marking have been introduced;
- A new need for labeling has been raised;
EN ISO 20345 safety ratings explained
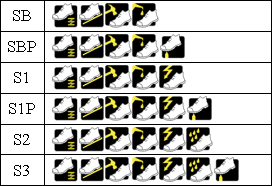
Safety shoes are divided into different safety rating classes according to the protection they offer, such as SB, S1, S2, S1P, and S3. In the table below, you can see an overview of what is included in each safety class.
|
|
Safety boots made from leather and other materials (not rubber/polymeric)
|
Rubber or PVC (waterproof safety gumboots)
|
|||||||
|
Rating
|
SB
|
SBP
|
S1
|
S1P
|
S2
|
S3
|
SB
|
S4
|
S5
|
|
200 joules toe cap
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
|
Penetration resistant midsole
|
|
✓
|
|
✓
|
|
✓
|
|
|
✓
|
|
Slip-resistant
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
|
Antistatic properties
|
|
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
|
✓
|
✓
|
|
Water penetration or waterproof
|
|
|
|
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
|
Oil and acid-resistant outsole
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
|
Shock-absorbing
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
EN ISO 20345 SB
Safety footwear that is classified as SB only has a protective toecap. It may have other safety features, but the standard does not require them. The sole may be of any material, including leather or plastic. The upper material must be non-conductive and protect against contact with live electrical circuits.
Safety boots classified as SB have no requirement for resistance to impact or penetration, but they must provide sufficient resistance to abrasion. This means that they are suitable for use in areas with no risk of falling objects or sharp objects that could cause foot injuries.
EN ISO 20345 SBP
Safety boots that are classified as SBP have a protective toecap and midsole. This type of safety footwear is intended for work in areas with a risk of falling objects. The protective toecap protects things falling from above, and the midsole protects against things falling from underneath.
SBP safety footwear must have a steel toe cap with a protection level of 200 Joules (J) or an equivalent protection level and hardness values greater than 20° HV. The midsole must be made from material that meets one of the following standards: EN ISO 20345 S1 P2 SRC or EN ISO 20345 S2 P2 SRC.
EN ISO 20345 S1
Safety footwear classified as S1 has a protective toecap and antistatic function. The standard requires that footwear protect against falling objects up to 100g.
The class S1 is specifically designed for use in environments with a risk of damage from sharp objects and heavy objects weighing more than 100g. The protective toecap of the shoes protects against sharp objects, while the antistatic feature prevents the accumulation of dust, which can cause an explosion in case there are sparks.
EN ISO 20345 S1P
Safety footwear classified as S1P has a protective toecap, midsole, and antistatic function. The protective toecap ranks the footwear as safety footwear with impact protection of at least 200 Joules. The midsole appears between the insole and outsole, and the antistatic function protects against static electricity discharge.
The protective toecap protects the toes from falling objects. It must also be able to withstand heavy impact. The midsole is located between the upper and outsole of the shoe. It protects the foot from slipping or rolling off a slippery surface. It also prevents injuries caused by falling objects or electric shock due to static electricity generated by friction with other materials.
The antistatic function reduces the risk of personal injury from electric shock caused by static electricity generated by friction when walking on wet floors or climbing stairs.
EN ISO 20345 S2
EN ISO 20345 S2 is a standard for safety footwear that is classified as S2. The S2 standard describes the requirements for safety footwear with protective toecap, waterproof function and anti static function.
The EN ISO 20345 S2-standard is divided into two parts: Part 1 covers the requirements for safety footwear with protective toecap and waterproof function, while Part 2 covers the requirements for safety footwear with protective toecap and anti static function.
EN ISO 20345 S3
Safety footwear that is classified as S3 has anti-static, made with a protective toecap and midsole. The upper of the shoe must be made from leather or leather substitute (non-porous material). The sole should be slip resistant and have a non-slip texture. There are also specific requirements for the heel height, heel stiffness and toe cap shape.
S3 shoes provide protection against physical hazards such as sharp objects, falling objects, electrical shock, heat and cold. They also protect against chemicals such as acids and alkalis.
EN ISO 20345 S5
EN ISO 20345 S5 is a safety footwear standard from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The EN ISO 20345 S5 rating is the highest level of protection that can be achieved by safety footwear. It combines the protective properties of ratings S1-4, and hence protects against a wide range of hazards, including electrical hazards.
S5 is used for rubber or plastic soled boots for industrial use or for use in laboratories and pharmaceutical facilities where extreme chemical resistance is required.
The EN ISO 20345 standard also covers footwear with non-slip and anti-skid properties as well as shoes with electrical hazard protection.
EN ISO 20345 slip resistance ratings explained
Slip resistance ratings are a measure of the coefficient of friction between two surfaces. If the coefficient of friction is less than 0.6, a floor can be considered slippery.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed a standard called ISO 20345:2011 to help manufacturers and designers assess and compare slip resistance ratings. Slip resistance ratings are measured using either the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) E18 or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) TR12402 standard test methods.
ISO 20345:2011 is broken down into three categories of slip resistance:
SRA: This rating is used to measure the coefficient of friction between a shoe sole and a surface such as a tile or concrete. The result is expressed as a value between 0 and 1, with 1 being the best. SRA is typically tested on ceramic tile with sodium lauryl sulfate (a diluted soap solution).
SRB: This rating measures the coefficient of friction between steel plates under dry conditions with glycerol added to simulate moisture on the surface. SRB results are expressed as values between 0 and 4, with 4 being the best.
SRC: This measurement combines SRA and SRB measurements into one value that reflects how well an
EN ISO 20345 Additional Ratings Explained
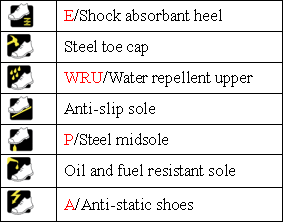
The following are some of the additional ratings explained:
C – Conductive
Conductive means that the material has a low resistance to electricity. If you have a static charge on your body, it can be dissipated through this material. This is especially important when working with computers and other electronics.
A – Antistatic
An antistatic material has a low level of static electricity buildup on its surface between 0.1 and 1000 Mega Ohms . This allows an object to be handled without fear of static discharge (small sparks) causing damage or injury.
I – Insulation against electricity
Insulation against electricity is used in applications where workers may be exposed to electric shock hazards. Commonly used for use when working with high voltage (relative term) equipment or inside power tools or equipment that may not be connected to a ground wire.
HI – Insulation against heat
Insulation against heat is used in applications where workers may come into contact with hot surfaces or materials that could cause burns or other injuries if touched by bare skin (such as molten metal).
CI – Insulation against cold
Insulation against cold is used for applications where workers may come into contact with cold surfaces or materials that could cause frostbite if touched by bare skin (such as ice).
E – Energy absorbing seat region
The energy absorbing seat region absorbs impact energy in case of a fall. It reduces the risk of injury and allows for a longer working life for your safety shoes.
AN – Ankle protection
It is important that your safety shoes protect not only your feet but also your ankles from injuries. AN stands for ankle protection, which means that the soles have extra protection in this area to prevent injuries due to falls or slips.
HRO – Heat resistant outsole
This rating indicates that the outsole material has been tested against temperatures up to 300 degrees Celsius (572 degrees Fahrenheit). This rating is especially important when working with hot machinery or welding equipment as it prevents burning or melting of the sole material.
WR – Water resistant
This means that the material can withstand water dripping onto it. It will not absorb water and will keep you dry in wet conditions.
WRU – Water resistant upper
This means that the upper portion of the shoe is made with a material that can withstand water dripping on it. It will not absorb water and will keep you dry in wet conditions. This rating is especially important when working around large amounts of standing water, such as oil tanks or shipyards.
M – Metatarsal protection
A metatarsal pad protects your foot from the impact on hard surfaces by absorbing some of the shock waves before it reaches your bones. This is especially important for workers who spend long periods of time on their feet doing repetitive tasks like walking or climbing stairs.
CR – Cut resistant upper
The CR rating is used to indicate that the material offers good cut resistance. This rating is not as common as the others because it is not required by ISO 20345-1:2011. It is primarily used in Europe and Australia where it is a requirement for safety footwear.
Which features should you choose in safety shoes?
Safety shoes can be made from a variety of materials and provide different levels of protection. Here we look at the most common types of safety footwear, what they offer and how you can work out which ones best suit your needs.
Toe protection (SB)
This is the most basic level of protection in safety shoes. A steel toe cap must be present to protect against impact injuries such as stubbing your toes or falling objects. The cap may be steel or composite material, but this level of protection is not enough if you are working on heavy machinery that could cause serious foot injuries.
Antistatic protection (A, S1, S1P, S2, S3)
Antistatic protective footwear is designed to prevent the build-up of static electricity on the surface of the shoe, which can cause a spark and lead to an explosion or fire. It’s particularly important for people working in areas where flammable liquids are stored, handled and transported, such as oil refineries and chemical plants.
Midsole penetration protection (SBP, S1P, S3, S5)
Footwear with midsole penetration protection is designed to stop sharp objects from penetrating through the sole. This is especially important for firefighters and police officers who may be required to walk over dangerous debris or through puddles of water that could contain broken glass or metal fragments.
Safety shoes with this kind of protection are usually constructed from an anti-static material such as vulcanized rubber or nitrile-coated leather. They typically have additional layers of material on top of these materials to protect against cuts and lacerations caused by studs or other sharp objects embedded in the ground below.
Energy absorption (E, S1, S1P, S2, S3)
This refers to energy absorption in the heel region. This is an important consideration if you’re working on concrete floors or walking over uneven terrain as it will help reduce injuries that occur when one foot strikes unexpectedly while another remains planted on the ground. The European Standard EN ISO 20345-1 requires footwear energy absorption values between 1-5J depending on the type of protection – E for electrical hazard; S1 for impact protection; S1P for both impact protection and electrical hazard; S2 for impact protection only; and S3 (the highest level) for electrical hazard only.
Water resistance (WR, WRU, S2, S3)
These shoes are designed to offer protection against water and moisture. They’re ideal for wet environments such as manufacturing, construction and agriculture.
Water-resistant footwear offers some protection against water ingress but isn’t designed to keep your feet dry. It’s suitable for light rain or other precipitation, but not immersion in water or high humidity conditions.
Heat resistance (HRO)
Safety shoes that have been designed with heat resistance offer protection against heat damage. This can be caused by hot surfaces or direct exposure to flames – either of which can cause serious burns. An HRO safety shoe will help protect your feet from the effects of these hazards by offering insulation against heat transfer. Safety boots with this feature are typically black in color so that they don’t reflect too much heat from the sun’s rays.
Insulation against cold and heat (CI, HI)
Cold-insulated safety shoes are made from a breathable material that keeps the foot warm in winter conditions. The material is usually waterproof, meaning it won’t soak up water like regular boots and shoes. Cold-insulated footwear is ideal for cold conditions where there’s snow or ice on the ground.
Hot-insulated safety shoes have an inner lining that helps to keep your feet cool in the summer months by absorbing sweat from within the shoe. They’re often worn with socks to prevent damage from heat build-up inside the shoe. Hot-insulated safety shoes are ideal for hot conditions where there’s no snow or ice on the ground (such as construction sites).
Additional Resources
- What are safety shoes?
- What is steel toe cap?
- What is composite toe?
- Composite toe vs Steel toe vs Alloy toe
- Steel toe vs Aluminum toe vs Carbon toe
- CE EN20345: Safety shoes standard
- What is the function of safety shoes?
- Top brands of safety shoes
- Safety shoes size chart
- Best safety shoes for construction